What you need to know, learn, and do to be successful in this vital role.
TL;DR: Everything you need to know to decide if you have what it takes to become an indexer on The Graph, plus more! Get added insights and advice from an experienced OG indexer.
Are you interested in becoming an indexer on The Graph Network? This article outlines the crucial steps, skills, and strategies you need to get started and succeed.
Plus, you’ll get incredible insights along the way from an experienced indexer, Vince from Nodeify.
The Graph is at the forefront of blockchain technology, revolutionizing how data is accessed and used across decentralized applications (dApps). It’s vital infrastructure that enables quick and efficient data retrieval, which is essential for a dApp’s optimal performance.
At the heart of this system are the indexers—key players who categorize and serve up data, ensuring that the blockchain ecosystem runs smoothly.
Getting an indexer up is one thing, but performance tuning to get the most out of your indexer is a big deal. You need to understand each component individually so that you can quickly identify the source when issues arise.
Vince from Indexer, Nodeify
Understanding the role of an indexer
What is an indexer?
On The Graph, an indexer is a crucial entity that collects, processes, and stores data from various blockchains, making it easily queryable. This work allows dApps to retrieve the specific data they need without having to process entire blockchains themselves.
Importance of indexers
Indexers efficiently organize blockchain data to ensure the seamless operation and accessibility of dApps. Their role is fundamental to the user experience, offering fast access to accurate and up-to-date information, which is essential for the functionality and reliability of decentralized networks.
Vince’s Insight: Different allocation strategies can make a big difference—whether you’re going all-in on APR, mixing APR chasing with query fees, or focusing solely on query fees.
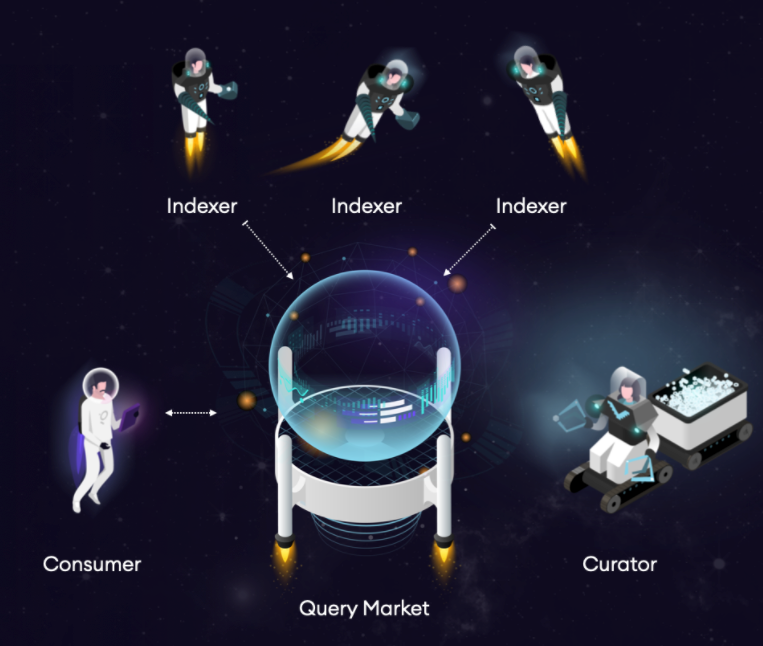
Graphic from The Graph blog
Indexers index subgraphs based on query signal and provide indexed data to the consumers. The curator signals on valid subgraphs (gets 10% of query fees) based on how much usage they perceive they will get. This helps indexers as they can focus on their job indexing and not worry if the subgraph is valid or will produce queries.
Excerpt from The Graph docs that explains more about indexers, delegators, curators, and consumers:
Indexers are node operators in The Graph Network that stake Graph Tokens (GRT) in order to provide indexing and query processing services. Indexers earn query fees and indexing rewards for their services. They also earn query fees that are rebated according to an exponential rebate function [similar to an IOU].
GRT that is staked in the protocol is subject to a thawing period and can be slashed if Indexers are malicious and serve incorrect data to applications or if they index incorrectly. Indexers also earn rewards for delegated stake from Delegators, to contribute to the network.
Indexers select subgraphs to index based on the subgraph’s curation signal, where Curators stake GRT in order to indicate which subgraphs are high-quality and should be prioritized. Consumers (e.g., applications) can also set parameters for which Indexers process queries for their subgraphs and set preferences for query fee pricing.
Prerequisites for becoming an indexer
Skills and knowledge
- Blockchain fundamentals: A solid understanding of blockchain technology’s core principles.
- GraphQL: Knowledge in GraphQL for querying data effectively.
- Networking and infrastructure: Skills in managing networks and infrastructure to ensure the reliability and efficiency of data indexing.
- Programming skills: No single language is specifically designed for blockchain. Developers can choose based on preference. However, proficiency in Rust, Python, Bash scripting, and TypeScript is particularly valuable.
- Data management and storage: The ability to manage and store data efficiently.
- Containerized tooling: Knowledge of Docker or Kubernetes, with Prometheus and Grafana to monitor tooling.
Understanding the ecosystem
A deep understanding of smart contracts, GraphQL, and blockchain protocols is beneficial and essential. This knowledge ensures that indexers can efficiently interact with and contribute to the blockchain ecosystem.
Vince’s Insight: It’s not just about the metrics. Being active in the community, collaborating, and helping others are invaluable. These are the things you can’t measure but make a significant impact.
Team composition
Operating as an indexer at an optimal level often requires a team with diverse skills:
- Techops: Managing clusters, databases, hardware, and configuration. Monitoring and scripting are part of this role.
- Cryptoeconomics: Utilizing smart contracts and analytics to strategize on allocations and prioritize support for different chains and data services.
- Marketing and community management: Building a brand, maintaining relationships with subgraph developers and delegators, and engaging in business development.
- Development: Some teams might engage in subgraph and Substreams development, supporting the ecosystem and establishing a business niche.
Financial & infrastructure requirements
Financial commitment
Becoming an indexer on The Graph requires more than technical know-how—it also requires a significant financial commitment. One requirement is staking a minimum of 100,000 GRT (Graph Tokens).
This stake is a testament to the indexer’s commitment to the network and serves as a security measure, ensuring that indexers act in the network’s best interest. It’s a critical part of the protocol’s economic model, designed to incentivize performance and integrity.
Infrastructure overview
Indexers require a scalable and robust infrastructure to manage and query vast data. The infrastructure setup varies based on the scale of operation:
- Small setup: Suitable for getting started with indexing several subgraphs. Requires expansion as demand grows.
- Standard setup: This default setup meets the example deployment needs, including k8s/terraform manifests.
- Medium setup: Geared for production level, supporting 100 subgraphs and handling 200-500 requests per second.
- Large setup: Designed to index all currently used subgraphs and manage the corresponding query traffic.
Each setup specifies requirements for Postgres (including CPUs, memory, and disk space) and virtual machines (VMs) detailing CPUs and memory needed.
Security precautions & basic infrastructure
Critical security measures include:
- Setting up an operator wallet for key separation.
- Making only the ports needed available to the public.
- Carefully managing database access.
The infrastructure’s core comprises the Graph Node, PostgreSQL database, data endpoints, IPFS nodes, and indexer components for network communication and management.
Detailed requirements & guidelines
For comprehensive details on the hardware specifications, security precautions, and infrastructure setup, refer to The Graph’s official documentation. These documents provide in-depth insights into effectively preparing for and managing an indexer’s responsibilities.
Setting up an indexer
Upon securing a minimum of 100k GRT tokens, you’ll launch your indexer by setting up and syncing your node with the Arbitrum One blockchain and The Graph’s network. You will also be required to run archive nodes for any subgraphs or networks you intend to support. This involves fine-tuning your hardware and software to meet technical requirements.
With your indexer operational, the next crucial step is to make your presence known: engage with the community, establish your brand, and clearly communicate your service offerings. This outreach is vital to attract delegators, signaling that you’re ready for business and equipped to handle queries and earn indexing rewards.
To help you get started on your indexer, use this GitHub repo developed by Indexer Payne with StakeSquid. This Graph Protocol Mainnet Docker Guide provides a one-stop solution for spinning up all the necessary containers for The Graph protocol mainnet using Docker Compose.
Insights from Vince on navigating challenges & maximizing opportunities
Common challenges for new indexers
Vince sheds light on the initial hurdles new indexers face:
Remember, building a name brand goes beyond recognition; it’s about fostering relationships and having a solid backup strategy for disaster recovery.
The role of community in an indexer’s journey
Vince believes that the community plays a crucial role in an indexer’s success:
The indexer community is a great place, and things like Indexer Office Hours (IOH) are incredibly welcoming. Introducing yourself and asking questions there can be very beneficial before diving into the technical deep end.
Embarking on the path of indexing: a conclusive reflection
If you’re intrigued by the potential to shape the landscape of decentralized technologies, evaluate your interests and abilities. Are you ready to take on the challenge of indexing?
We invite you to take the first step towards becoming an indexer. Explore The Graph community, engage with current indexers in Discord, read over Know Your Indexer interviews, and start your journey today. Your contribution could be pivotal in enhancing the blockchain ecosystem for everyone.
💡 This article answers questions like:
- What is an indexer on The Graph?
- What is an indexer's role in the accessibility of blockchain data?
- What skills and knowledge do you need to become an indexer?
- What infrastructure is required to be an indexer?
- What are common challenges for an indexer?







I hope this is a good starting point for anyone out there interested in becoming an indexer. It’s a hard but rewarding job with a great project with a bright future.
This is a great overview, Paul. Well done!
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through anything like this before.
So good to find another person with original thoughts on this topic.
Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This site is one thing that is
required on the internet, someone with some originality!
Thank you for the insights. I’ll definitely use this guide to learn more and hopefully start indexing someday.